Diabetes mellitus is a pathological condition characterized by violations of metabolic processes (metabolism). This occurs due to insufficient production of insulin of its own hormonal substance, as in the case of type 1 diabetes mellitus or a violation of its effect on cells and tissues of the body (type 2 pathology).
The article discusses in detail the main types of diabetes mellitus, the differences in its causes and mechanisms of development, as well as a description of the treatment characteristics of patients.
A little about insulin and its role in the human body
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas. This organ is located at the back of the abdomen, it is surrounded by the spleen and the loop of the duodenum. The weight of the pancreas is about 80 g.
In addition to hormones, the glands produce pancreatic juice, which is needed for the digestion of lipids, carbohydrates and proteins. The hormone insulin is synthesized by β cells. They are localized almost all over the surface of the pancreas in the form of small groups called the islands of Langerhans. The islet also contains α cells that synthesize the active ingredient of the hormone glucagon. This hormone has the opposite action to insulin.
Healthy adults have about a million of these small islands with a total weight of a few grams.
Insulin is a protein molecule made up of several amino acid chains. Its job is to assimilate glucose (sugar) by the cells of the body. Sugar is needed for a person to get energy. Without it, cells and tissues cannot function.
In parallel with sugar intake, insulin also controls the penetration of amino acids into cells. Amino acids are considered to be one of the main building materials. Another function of insulin is the accumulation of lipids in the body.
Classification of diabetes
According to the generally accepted classification of diabetes mellitus and used in modern endocrinology, pathology is divided into the following types:
- Type 1 - insulin dependent (IDDM);
- type 2 - non -insulin dependent (NIDDM);
- forms of pregnancy;
- certain types of diabetes.
The last option is a group of pathological conditions that differ from each other in their pathogenesis and causes of their development. These include hereditary defects at the genetic level on the part of the insulin hormone or insulin secretion cells, diseases caused by the action of chemicals and drugs, diabetes due to infectious processes, etc.
All types of diabetes are united by hyperglycemia. This is a condition indicated by high glucose levels in the blood. It is against the background of diagnosing glycemic numbers based on the confirmation or rejection of a diabetes diagnosis.
1 type
Type 1 pathology (ICD -10 - E10 codes) is considered an autoimmune process, resulting in the death of insulin secreting cells. Speaking in simple language, such a process is launched in the human body, where their own immune cells regard the pancreatic cells as foreign and destroy them.
As a rule, insulin -dependent types arise as a result of hereditary predisposition, but corresponding provocative factors also play an important role. Statistics show that the presence of pathology in children is possible in the following cases:
- if the mother is ill - with a frequency of 2%;
- sick father - 5%;
- sick brother or sister - 6%.

If one of the relatives has the disease, other family members may be healthy, even if they are at high risk.
The presence of autoimmune processes, that is, antibodies in the body to the pancreatic cells themselves, occurs in more than 80% of insulin -dependent patients. Often, along with type 1 disease, diabetics suffer from other autoimmune diseases, for example, chronic adrenal insufficiency, pancreatic disease, vitiligo, rheumatism.
How did it develop?
Typically, the clinical signs of the disease appear when more than 85% of insulin-secreting cells have died, but depending on the individual characteristics of the organism, this period may vary in duration. Often occurs in childhood and adolescence. It happens that young patients learn about the presence of the disease already in the period of acute complications, for example, in ketoacidotic conditions.
Lack of energy and lack of insulin lead to a massive breakdown of fats and proteins, which explains the patient’s weight loss. High blood sugar causes hyperosmolarity, which is indicated by massive urine output and the development of dehydration symptoms. Because insulin is insufficient, the body experiences energy starvation, as a result, excessive synthesis of contrainsular hormones occurs, that is, which has the opposite effect in relation to the work of insulin.
These hormones include cortisol, glucagon, and somatotropin. They cause a stimulation of glucose formation in the body, despite the fact that blood sugar levels are already through the roof.
The massive breakdown of fats leads to an increase in the number of free fatty acids in the blood. This is a trigger for the formation and accumulation of ketone bodies (acetone), which are provocateurs of ketoacidotic conditions. If such pathology, dehydration and the shift of blood pH to the acidic part continue to develop, the patient may fall into a coma, and even death is possible.
symptoms
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by the development of bright symptoms, which worsen over several weeks. Diabetic patients complain:
- for the formation of large amounts of urine;
- excessive thirst;
- persistent itching of the skin;
- weight reduction.
The manifestations of the disease are considered quite specific, but still require differential diagnosis.
Weight loss, accompanied by normal or increased appetite, is one of the symptoms that distinguishes type 1 pathology from other types of diabetes mellitus. The patient is worried about a sharp weakness, he can not do normal work, drowsiness occurs.
The development of the clinical picture is accompanied by the appearance of the smell of acetone in the exhaled air, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, and symptoms of severe dehydration. If the disease appears at a later age (about 40 years), the symptoms are not so pronounced, and, as a rule, the presence of the disease is determined during clinical examination.
type 2
Insulin -free diabetes mellitus (ICD -10 code - E11) is a chronic pathology, in which high blood sugar levels occur as a result of insulin resistance. Later, the work of the Langerhans island cells was also disrupted. In parallel with carbohydrate metabolism, pathology also affects the process of fat metabolism.
Hereditary predisposition is one of the leading causes of type 2 diabetes. If one of the parents has the disease, the child will get sick in 40% of cases. However, heredity alone is not enough, the provocative factors are:
- high weight;
- low physical activity;
- high blood pressure numbers;
- high levels of triglycerides in the blood;
- the presence of infants born weighing more than 4 kg in the past;
- the presence of diabetes during pregnancy in the past;
- polycystic ovaries.
Currently, the number of patients with type 2 diabetes is increasing. This form of pathology accounts for more than 85% of all clinical cases. Middle -aged and older men and women are more often ill.
How did it develop?
The mechanism of development is based on the fact that insulin resistance appears, that is, the pancreas produces a sufficient amount of hormones needed to transport sugar molecules into the cells, but the cells themselves lose sensitivity to this substance. The result is hyperglycemia.
To reduce blood sugar levels, the gland begins to work at the limit of its capacity. This triggers a lack of insulin secretion cells.
For the second type of pathological condition, the appearance of ketoacidosis is uncommon, because even a small amount of hormones are synthesized by the islets of Langerhans.
symptoms
The disease usually manifests itself in patients over 40 years of age. In most cases, the clinical picture is combined with the appearance of pathological weight gain, changes in fat metabolism in blood tests. Related symptoms:
- performance is slightly reduced, but this is not so marked as in the first type of disease;
- pathological thirst;
- excretion of large amounts of urine;
- women may be bothered by itching on the skin in the genital area and perineum;
- a rash appears on the skin, which does not heal for a long time;
- discomfort, numbness and chills in the lower legs.
Type of pregnancy
The WHO classification of diabetes mellitus includes the gestational form of the disease (ICD -10 - O24 code). It is typical for pregnant women. 5-7% of patients who give birth have diabetes. The WHO classification of diabetes and its types includes another name for this type of pathology - diabetes in pregnant women.
If the disease appears in a woman before the moment of conception of a child, it is considered pragestational, during the period of pregnancy - pregnancy. At present, the mechanisms of development and causes of the disease are not fully understood. There are data on the role of hereditary predisposition. Possible risk factors:
- physical and mental trauma;
- contagious disease;
- pancreatic disease;
- inclusion in the menu in large quantities of foods rich in carbohydrates.

Obstetricians and gynecologists agree that adequate physical activity can reduce the risk of developing pathology.
This form of pregnancy can manifest as a manifestation, that is, a clear clinical picture, or as a violation of glucose tolerance. Pathology, as a rule, disappears by itself after the baby is born.
The woman became a member of a group of patients at high risk for developing an insulin-independent type of diabetes mellitus over the next 10-15 years.
During the period of childbirth, a woman’s body undergoes certain changes related to the hormonal sphere. This is due to the function of the placenta, which secretes the following hormones:
- chorionic gonadotropin;
- progesterone;
- estrogen;
- corticosteroids, etc.
All of these hormone active ingredients cause the appearance of insulin resistance. At this stage, cell hyperplasia of insulin secretion and the release of large amounts of insulin into the blood are observed from the pancreas. The emergence of insulin resistance leads to the fact that the female body begins to actively use fat metabolic products, while sugar is stored to nourish the fetus. Under a combination of hereditary predisposition to diabetes and the above factors, the disease develops.
symptoms
This type of pregnancy disease manifests itself in the same way as other types of diabetes, but the symptoms are somewhat less pronounced. A woman may not pay attention to symptoms, associating its occurrence with her "attractive" position. If the clinical picture is stated, pregnant women can submit the following complaints to the attending physician:
- dry mouth;
- constant desire to drink;
- excretion of large amounts of urine;
- increased appetite;
- declining performance and weaknesses;
- appearance of itching and burning in the genital area.
Important! Usually the disease develops in the late second or early third trimester.
Pathological effects on mother and fetus
Chronic hyperglycemia has a negative impact on both the mother’s body and the child’s own. Pregnancy can be complicated:
- polyhydramnion;
- late gestosis;
- termination of pregnancy at different periods of pregnancy;
- birth of a child with a large body weight (more than 4-4. 5 kg).
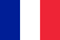
Babies born to sick mothers have a special appearance. Their shoulders are quite wide, subcutaneous fat is pronounced, the face has a round moon shape. There is significant swelling of the skin and hypertrichosis. The most severe complications of the disease are fetal death during fetal development and death of the newborn. As a rule, such conditions occur in the presence of pragestational forms of the disease.
Children born to sick mothers differ from their peers in their large weight and characteristic appearance.
Certain types
We are talking about secondary forms of pathological conditions that develop under the influence of chemicals, drugs, infectious processes and other diseases of the endocrine and extra-endocrine spheres.
Diabetes can be caused by the following diseases and conditions of the pancreas:
- inflammation of organs;
- mechanical damage;
- glandular removal;
- neoplasm;
- Cystic Fibrosis;
- pigment cirrhosis, etc.
Instead of chemicals and drugs, nicotinic acid, adrenal cortex hormones, interferon, thyroid hormones, and diuretics can contribute to the development of the disease. The list goes on with opiates, poisons intended for the destruction of rats, antidepressants, drugs used for antiretroviral therapy.
Of the causative agents of infectious diseases, the provoking factors are rubella virus and cytomegalovirus.
Characteristics of treatment
The therapy of the pathological condition is selected individually for each clinical case. The scheme and method of treatment used depends on the degree of diabetes, its type, the brightness of the clinical picture, and the presence of complications. How to determine and confirm the presence of the disease, a qualified endocrinologist will tell you. He will give instructions on the following diagnostic methods:
- general blood and urine tests;
- capillary blood analysis for glucose from fingers on an empty stomach;
- blood biochemistry;
- urinalysis for sugar;
- glucose tolerance test - it is mandatory for all pregnant mothers in the period from 22 to 26 weeks of pregnancy;
- determination of glycosylated hemoglobin indicators.
Therapeutic measures include not only taking medication, but also physiotherapy training, dietary correction, teaching patients self-control.

It is important that relatives support the sick person’s desire to reduce the aggression of the pathological condition and achieve compensation.
self control
Diabetics should keep records of their mood, glycemia, urine sugar levels, as well as record data on individual menus and physical activity throughout the day. The whole of the indicator and its accounting is self -controlled. The purpose of such events is not only to control sugar levels, but also to interpret the results, as well as plan their actions if the number exceeds the acceptable range.
With normal health, it is important to measure sugar levels at home and record this indicator at least once a day. Any changes in well -being require an explanation of the amount of glucose in the blood several times a day:
- before each main meal;
- some time after food enters the body;
- before night rest;
- in some cases, you may need morning measurements on an empty stomach.
Glucose in urine is also measured at home. This requires the presence of an express line. They can be purchased at the pharmacy. The presence of sugar in the urine will indicate that the blood glucose level exceeds 10 mmol / l, as this figure is the kidney threshold at which glucose molecules penetrate the urine.
If the patient is on the go, is actively involved in sports or has any comorbidities, more rigorous self -monitoring will be required.
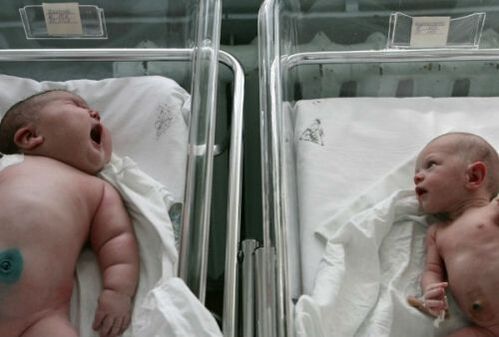
For a comfortable daily life for a person with diabetes, it is necessary to purchase the following individual devices and devices:
- glucometer with lancet, test strip and necessary accessories included;
- express urinary tract, which measures body levels of acetone and sugar;
- tonometer to explain the number of blood pressure;
- self -control diary, in which all necessary data will be recorded.
Food
Individual dietary correction is fundamental to the treatment of any type of diabetes mellitus. With type 1, changing the personal menu allows you to reduce the load on the pancreas, reducing the amount of carbohydrates supplied to the body. In type 2 diabetes, a low -calorie diet can not only achieve the above goals, but also reduce pathological weight.

Patients are advised to observe table number 9, which may have several options (a, b, c).
Patients must strictly adhere to daily caloric intake. It is calculated individually for each patient, depending on weight, age, gender, energy expenditure, physical activity, drug therapy used. In the diet of patients, it is necessary to limit the intake of carbohydrates and high -calorie foods. Protein is not only possible, but also necessary, fat should be limited slightly, especially with type 2 pathology.
Patients need to understand the system of bread units, glycemic index and insulin products, calories. Characteristics of nutritional principles:
- do not eat more than 8 units of bread in one serving;
- sweet liquids (lemonade, tea with sugar, store -bought juices) are prohibited;
- instead of sugar, sweeteners are used, and instead of store-bought juices, homemade compotes and fruit drinks are used;
- the number of bread units must be planned in advance, as insulin is given before the product enters the body;
- food should be in small portions, but frequent;
- the patient should receive an adequate amount of fluid - restriction is possible in the presence of renal failure or other complications accompanied by edema.
You can read more about the forbidden foods, as well as those that should be eaten without fear, in the table.
| The highest calories to limit | Authorized Products | Amount of alcohol allowed (subject to conditions of use - below) |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The possibility of drinking alcohol is discussed individually. A small amount is allowed if there is compensation for diabetes mellitus, there are no complications, the patient feels normal. Beer and sweet cocktails are prohibited.
Medical treatment
Treatment of IDDM and other forms of pregnancy is based on insulin therapy. This is the process of introducing insulin -based hormone preparations to replace the lack of its own nutrients in the body. There are several groups of drugs that differ in duration of action and speed of onset of effect: ultrashort, short, moderately resistant hormone and insulin -prolonged preparations.
Typically, doctors combine two drugs with different durations of action at the same time. This is necessary to create the most physiological conditions for the pancreas.
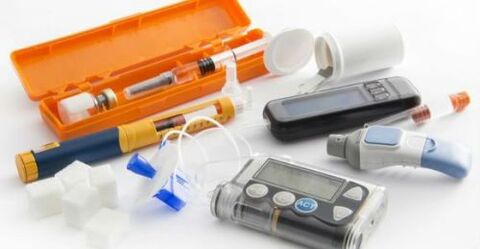
These medications are given with an insulin syringe, a syringe pen or using an insulin pump in automatic mode.
Type 2 disease requires the use of hypoglycemic tablets. The main groups are biguanides, sulfonylurea preparations, thiazolidinediones, glinides, etc.
The differential diagnosis between the types of diabetes mellitus should only be carried out by a qualified specialist. He or she will also help you choose a therapy regimen, an optimal lifestyle, and provide recommendations that allow patients to achieve compensation as quickly as possible.